Water acts as an acid when it contacts calcium carbonate dissolving the limestone.
What does granite turn into after weathering and erosion.
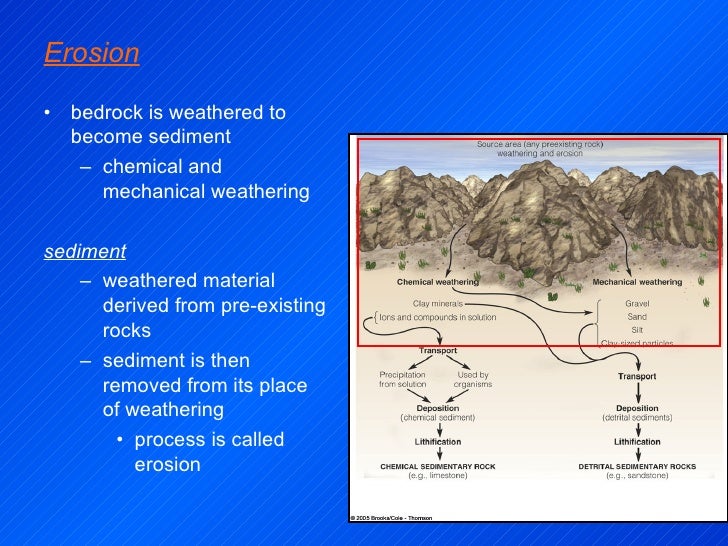
Mechanical weathering includes pressure expansion frost wedging root wedging and salt expansion chemical weathering includes carbonic acid and hydrolysis dissolution and oxidation.
What happens when a rock like granite undergoes the processes of weathering what does it turn into.
5 2 weathering and erosion.
Granite is an igneous rock that injects or intrudes as magma into earth s crust and then cools.
Chemical weathering is different from mechanical weathering because the rock changes not just in size of pieces but in composition.
It consists of four main mineral compounds.
In the cairngorms chemical weathering of the granite is restricted in its extent and depth.
Weathering and erosion slowly chisel polish and buff earth s rock into ever evolving works of art and then wash the remains into the sea.
Many horizontal and vertical cracks run through limestone.
Granite is extremely hard and less affected by the freeze thaw cycle the forces of abrasion and the surface exfoliation processes that are all a part of physical weathering.
Basically it is the granular disintegration or grusification of granite due to the hydration of feldspar and biotite minerals which break down into clays.
A gravestone made of granite will therefore resist fracturing cracking and chipping longer than a sandstone marker found in the same location.
That is one type of mineral changes into a different mineral.
The low relief also reduced erosion rates prior to glaciation and allowed deep weathering profiles to develop.
The processes are definitively independent but not.
These cracks allow water to pass easily through the rock.
Ice weathering is when water seeps into a rock.
Chemical weathering works through chemical reactions that cause changes in the minerals.
The swelling of these clay minerals as they abosorb water further weathers the granite and biotite minerals in particular also undergo oxidiation leading to the reddish color of grus.
It then creates a crack or even split the rock entirely.
Plagioclase feldspar is a compound of sodium and.
Chemical weathering is the other important type of weathering.
Bedrock refers to the solid crystalline rock that makes up the earth s outer crust.
The dissolved calcium carbonate may drip into underground caves hollowed out from the action of weathering.
Weathering is a process that turns bedrock into smaller particles called sediment or soil.
The exposures provided by glacial cliffs demonstrate that the granite is generally covered only by a thin regolith.