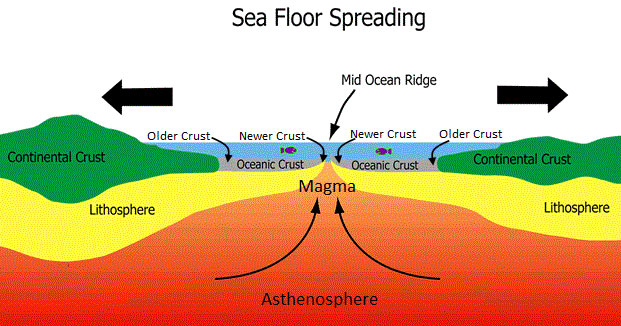
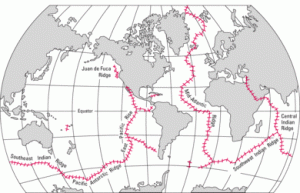
The theory of seafloor spreading seafloor spreading is a geologic process where there is a gradual addition of new oceanic crust in the ocean floor through a volcanic activity while moving the older rocks away from the mid oceanic ridge.
What is seafloor spreading theory upsc.
The theory of sea floor spreading states that new oceanic crust is being formed continuously at mid oceanic ridges while the older rocks move away from the ridge.
Sea floor spreading theory is important for the upsc prelim and main exam.
Thus the midocean ridges contain the newest crust formed on the planet.
Cold seawater cools and solidifies this magma to form new.
Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones known collectively as the mid ocean ridge system and spreads out laterally away from them.
Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics.
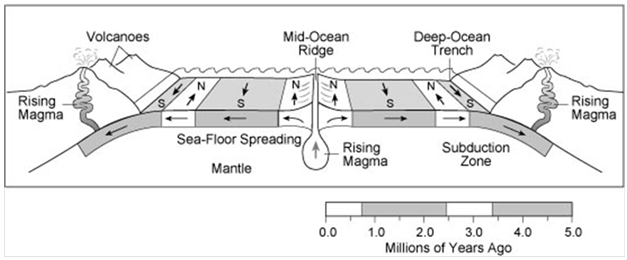
Hess argued constant eruptions at the crest of oceanic ridges ruptures the ocean crust and new lava wedges into it pushing the oceanic crust either side the ocean floor this spreads how it causes volcano n earth quake.
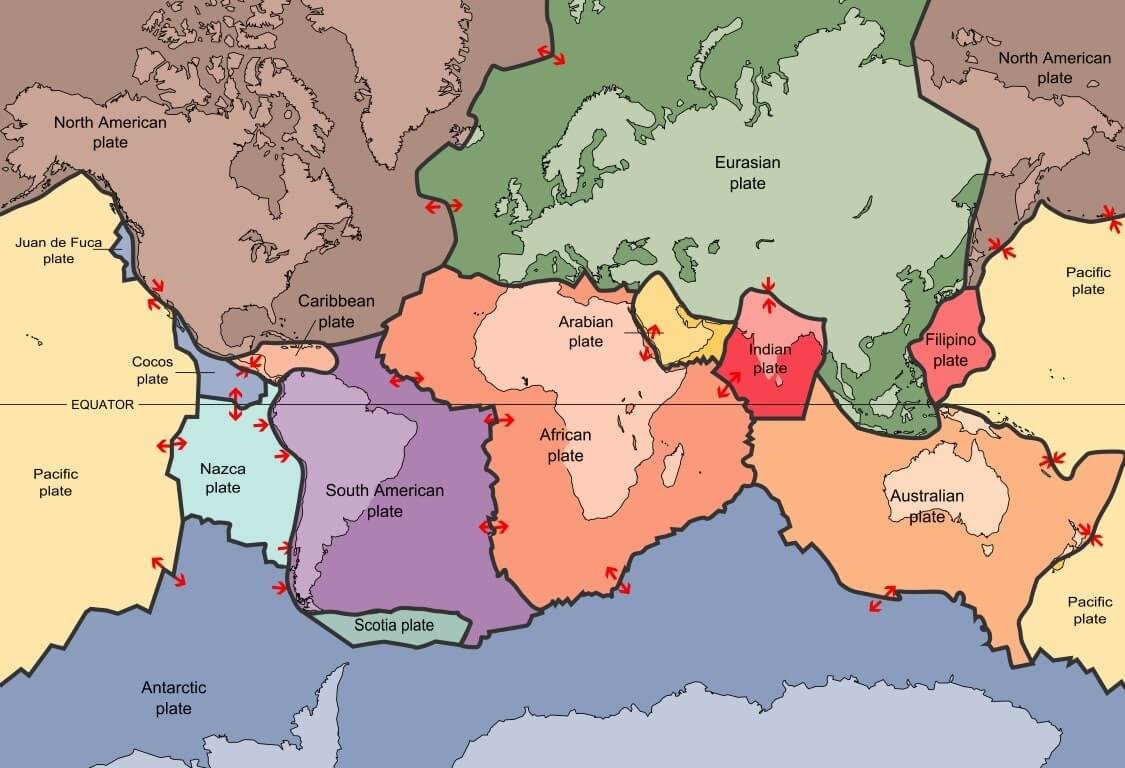
When oceanic plates diverge tensional stress causes fractures to occur in the lithosphere.
Keeping earth in shape.
Supporters of continental drift originally theorize d that the continents moved drifted through unmoving oceans.
Known as seafloor spreading this theory stated that mid ocean ridges are formed by currents of magma rising up from the mantle.
Seafloor spreading proves that the ocean itself is a site of tectonic activity.
After the second world war the understanding of ocean floor significantly changed.
Volcanic eruptions create new basaltic ocean floor that then spreads away laterally from the ridge.
That is it explains why the age thickness and density of the oceanic crust increases with distance from the mid oceanic ridge.
It opened up a whole new paradigm for the study of geomorphology.
This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century.
Seafloor spreading disproves an early part of the theory of continental drift.